Connection Setup Instructions
Setup port forwarding using Mikrotik router
The recommended procedure is to create one secure access-list named "SmartOLT" which includes the SmartOLT servers IP addresses that will be permitted to communicate with the OLTs.
The following example uses a "dummy" 192.168.200.2 OLT IP address. Replace 192.168.200.2 with your OLT private IP and adapt the script to match your network scenario.
# Create an address-list with SmartOLT servers
/ip firewall address-list add address=amz.smartolt.com list=SmartOLTIf you are not using Mikrotik, please contact support for the complete list of IPs to be allowed.
# Setup port forwarding.
Ex.: For packets received from source-address-list SmartOLT the action will be dst-nat to => OLT_Private_IP_Address
To use more OLTs on the same public IP address, increment each external port (Ex. for OLT2 : 2334, 2323, 2162)
/ip firewall nat add action=dst-nat chain=dstnat \ dst-port=2333 protocol=tcp src-address-list=SmartOLT \ to-addresses=192.168.200.2 to-ports=23 comment=SmartOLT /ip firewall nat add action=dst-nat chain=dstnat \ dst-port=2322 protocol=tcp src-address-list=SmartOLT \ to-addresses=192.168.200.2 to-ports=22 comment=SmartOLT /ip firewall nat add action=dst-nat chain=dstnat \ dst-port=2161 protocol=udp src-address-list=SmartOLT \ to-addresses=192.168.200.2 to-ports=161 comment=SmartOLT
Do not forget to replace 192.168.200.2 with your OLT private IP address.
# Allow the OLT to contact SmartOLT servers
/ip firewall nat add action=masquerade chain=srcnat \ dst-address-list=SmartOLT comment=SmartOLT
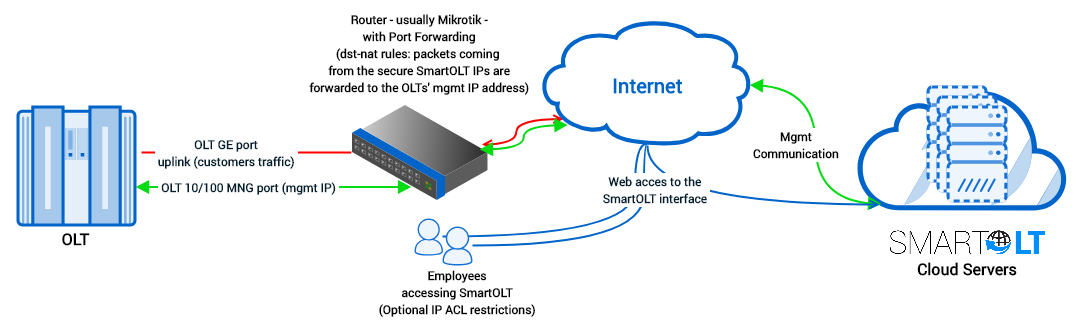
Packet-flow diagram using out-of-band [10/100 or mng1 or meth] management port:
ZTE & Huawei OLTs
-
- ZTE C300,C320,C350M,C220
- All firmware versions v1.2.x, v2.0.x, v2.1.x


-
- Huawei MA56xx,58xx series
- All firmware editions R009 -> R018
-



